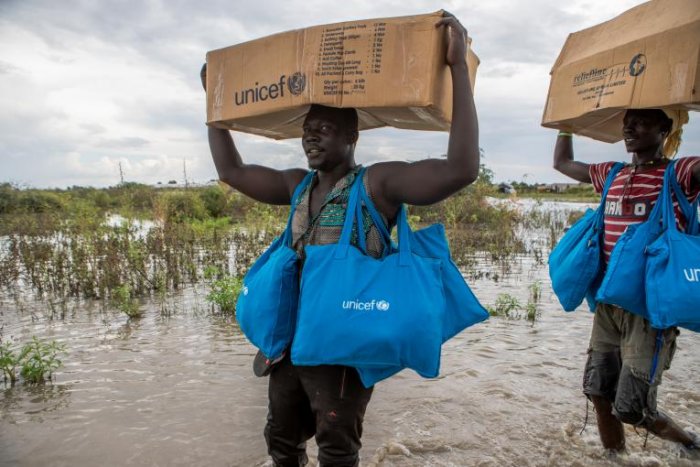
A record 4.5 million children – two out of three – in South Sudan are in desperate need of humanitarian support, UNICEF warned today, ahead of the 10th anniversary of the country’s independence. In a report on the impact of the humanitarian crisis on children, UNICEF warned that hopes that independence would bring a new dawn for the country’s children have faded. Bouts of violence and conflict, recurring floods, droughts and other extreme weather events fuelled by climate change, and a deepening economic crisis have led to extremely high food insecurity, and one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises. The recent peace agreement, which has only partially been implemented, has so far failed to bring about any remedy to the challenges facing the country’s children and young people.
“The hope and optimism that children and families in South Sudan felt at the birth of their country in 2011 have slowly turned to desperation and hopelessness,” said UNICEF Executive Director Henrietta Fore. “The childhood of many 10-year-old children in South Sudan today has been beset by violence, crises and rights abuses.”
Some 8.3 million people in South Sudan need humanitarian support, a much higher number than the levels seen during the 2013-2018 civil war, which ranged from 6.1 million to 7.5 million people.
The child mortality rate is among the highest in the world, with 1 in 10 children not expected to reach their fifth birthday.
High levels of food insecurity are of particular concern. Some 1.4 million children are expected to suffer from acute malnutrition this year, the highest figure since 2013. More than 300,000 children – the highest number ever in the country – are expected to suffer from the worst form of malnutrition and are at risk of dying if treatment is not provided.
Limited access to education and high drop-out rates have left 2.8 million children out of school – the highest proportion of out-of-school children in the world at more than 70 per cent of school-age children. The 14-month school closure because of the COVID pandemic had pushed an additional 2 million children out of school.
Despite continued insecurity, UNICEF is working with partners to increase the capacity to screen and treat children for acute malnutrition with an expected caseload of 1.4 million children in 2021. Improved access to clean water, improved sanitation and hygiene and access to basic health care are also among UNICEF’s top priorities, together with access to education.
Source: UNICEF